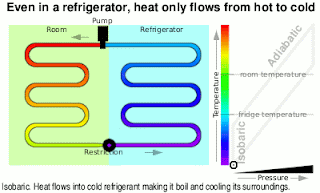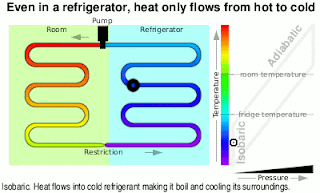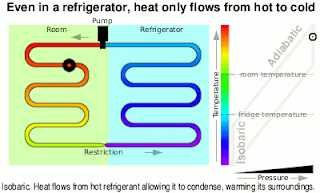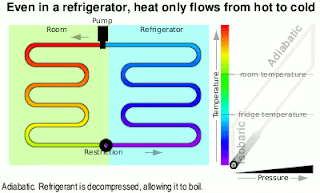
Kinetic Energy And Work
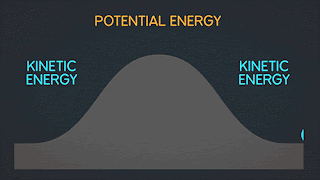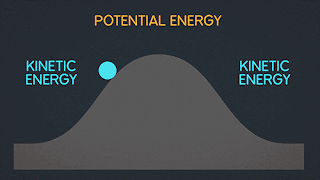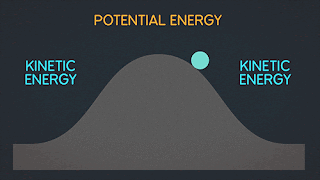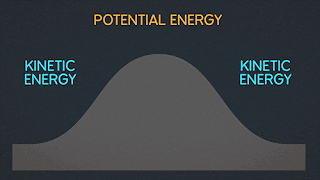
KINETIC ENERGY Kinetic Energy "K" is energy associated with the "state of motion" of an object. The faster the object moves the greater is its kinetic energy. When the object is stationary. Its kinetic energy is zero. NOTE: ^2=exponent number raised by the number two. / = is a division operator. * = multiplication operator Kinetic energy formula is K=1/2mv^2 The SI unit of Kinetic energy (and all types of energy) is the joule (j) named for James Prescott Joule, an English scientist of the 1800's and defined as 1 joule = 1 J = 1 kg*m^2/s^2 Example video on kinetic energy : WORK Work W is energy transferred to or from an object by means of a force acting on the object. Energy transferred to the object is positive work and energy transferred from the object is negative work Work have an three sub topics include forces and displacement they are: Work done by gravitational fo...